Kids who play team sports are less likely to have mental health issues, study suggests
[ad_1]
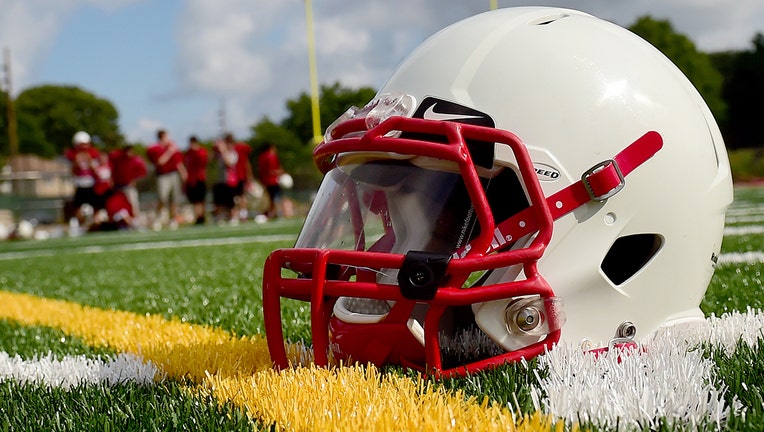

A football helmet lies on the floor while users of the Floral Park Large University soccer group are in the background practising for the 2015 time, on the early morning of August 19, 2015.(Photograph by Thomas A. Ferrara/Newsday by way of Getty Photos)
A new study discovering the affiliation among a kid’s participation in an arranged activity and their psychological well being located that these who participate in group sports activities may possibly be much less likely to have psychological wellbeing issues.
In accordance to the review, released in PLOS One, researchers employed facts from extra than 11,000 U.S. small children concerning the ages of 9 and 13 years aged.
Mom and dad and guardians provided self-reports of their child’s psychological overall health problems using a “kid conduct checklist.” In addition, they were provided with a prolonged list of actions (sporting activities, tunes, hobbies) and have been questioned to suggest their child’s life time involvement in each and every.
Scientists observed that participation in a team sport when compared to non-sport participation was connected with 10% reduce nervous/frustrated scores, 19% lessen withdrawn/frustrated scores, 17% reduce social troubles scores, 17% decreased imagined complications scores and 12% reduced awareness problems scores.
Colts kicking the stigma of psychological health
LiveNOW2
Conversely, participation in an person activity in comparison to non-activity participation was involved with 16% better nervous/depressed scores, 14% bigger withdrawn/frustrated scores, 12% greater social challenges scores and 14% larger attention difficulties scores.
“It is attainable that some kids and adolescents who compete in person sports activities encounter sizeable pressure associated with accomplishing independently, which could contribute to mental health challenges,” the study’s authors explained.
In addition, athletes who performed the two a crew and person activity did not have diverse psychological health profiles in contrast to non-activity taking part in young children and adolescents.
“Benefits point out that crew activity participation was related with less mental wellbeing troubles, whereas unique sport participation was linked with greater mental well being difficulties,” the study’s authors ongoing. “The effects counsel that [the] form of activity may well be a salient aspect in the partnership concerning sport participation and psychological health.”
All round, there were much less psychological health complications amongst women as opposed to males, and among people who determined as Black and Asian when compared to all those who recognized as White.
“The outcomes of this review, coupled with earlier investigate results, propose that participation in arranged workforce activity may possibly be a valuable medium via which to endorse kid and adolescent psychological wellbeing,” the authors included. “Endeavours to deliver youngsters and adolescents with inexpensive alternatives to join structured group sport leagues/clubs outdoors of university may require additional awareness, specifically for households with socioeconomic challenges.”
A possible limitation the scientists noted was its use of mum or dad self-reports, noting that it is feasible that dad and mom who enroll their kids in unique sports activities have a tendency to overestimate the problematic facets of their children’s psychological and behavioral conduct. Alternatively, they said it is also plausible that mom and dad who sign-up their youngsters in group sports activities are far more likely to look at their children interacting positively with friends and thus have a tendency to undervalue any opportunity mental wellbeing troubles.
Researchers explained extra analysis will be essential to figure out to what extent, and less than what situation, participation in an particular person activity may possibly be problematic for adolescents.
Also, the authors mentioned upcoming reports could be completed to analyze the hyperlink amongst sport participation and psychological wellbeing between minority youth populations (these as LGBTQ adolescents) who may be at an greater threat for mental well being issues.
These results do enhance past exploration suggesting that workforce activity participation may possibly be a auto to support youngster and adolescent mental overall health. But other scientific tests have also connected youth activity participation with adverse outcomes these types of as panic and burnout.
Related: Concentrating on 1 sport can have both optimistic and unfavorable results in teens, analyze finds
In a modern analyze, released last thirty day period in the Orthopaedic Journal of Sporting activities Medication, scientists surveyed 975 U.S. large school athletes and observed two proportions of competitiveness — the enjoyment of competition which has been associated with intrinsic sport inspiration and superior sportsmanship, along with contentious competitiveness which has been connected with extrinsic sport commitment and poor sportsmanship.
[ad_2]
Resource link